Terraform is a powerful Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that allows you to define and manage your cloud resources declaratively. In this post, we’ll explore how to use Terraform to create Azure Resource Groups, a foundational step in organizing and managing your Azure resources.
Why use Terraform for Azure Resource Groups?
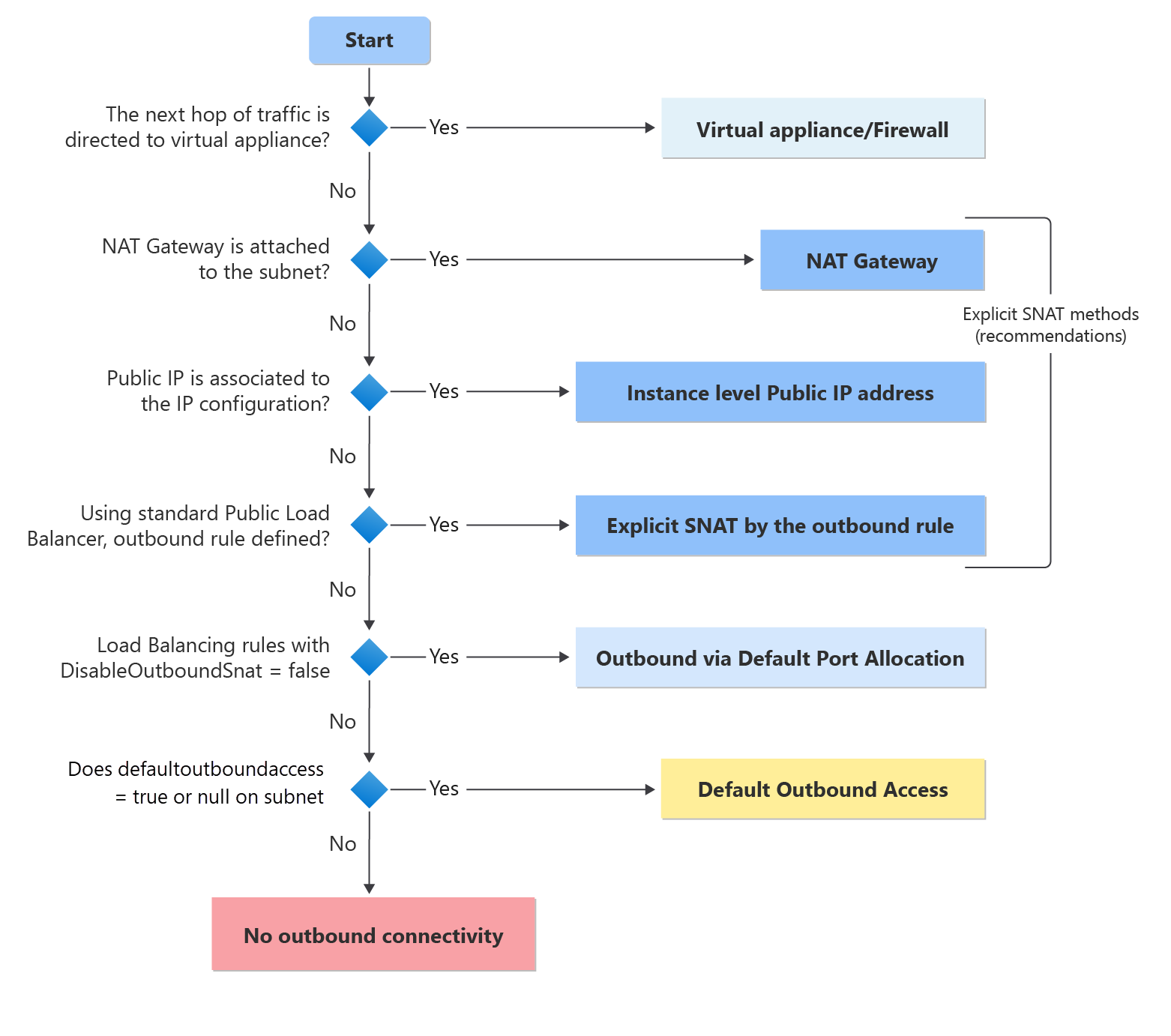
Azure Resource Groups act as containers for your resources, making it easier to manage and organize them. By using Terraform, you can automate the creation and management of these groups, ensuring consistency and reducing manual effort.
Terraform’s declarative approach ensures that your infrastructure is always in the desired state.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- Terraform installed: Download and install Terraform from terraform.io.
- Azure CLI installed: Install the Azure CLI from Microsoft’s documentation.
- Azure account: Sign up for an Azure account if you don’t already have one.
Step-by-step guide to creating a Resource Group
1. Initialize your Terraform project
Create a new directory for your Terraform configuration files and navigate to it:
mkdir terraform-rg && cd terraform-rg
2. Write the Terraform configuration
Create a file named main.tf and add the following configuration:
// main.tf
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "example" {
name = "example-resource-group"
location = "East US"
}
This configuration specifies the Azure provider and defines a resource group named example-resource-group in the East US region.
3. Initialize Terraform
Run the following command to initialize the Terraform project and download the Azure provider:
terraform init
4. Preview the changes
Use the terraform plan command to preview the changes Terraform will make:
terraform plan
This will show you the resources that will be created.
5. Apply the configuration
Apply the configuration to create the resource group:
terraform apply
Type yes when prompted to confirm the changes.
6. Verify the resource group
You can verify the resource group in the Azure portal or by using the Azure CLI:
az group show --name example-resource-group
Best practices for managing Resource Groups with Terraform
- Use variables: Parameterize your configuration to make it reusable across environments.
- State management: Use a remote backend like Azure Storage to store your Terraform state securely.
- Version control: Store your Terraform configuration files in a version control system like GitHub.
Example with variables
Here’s an updated configuration using variables:
// variables.tf
variable "resource_group_name" {
default = "example-resource-group"
}
variable "location" {
default = "East US"
}
// main.tf
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "example" {
name = var.resource_group_name
location = var.location
}
To apply this configuration, create a terraform.tfvars file with your desired values:
resource_group_name = "my-resource-group"
location = "West US"
Conclusion
Using Terraform to create Azure Resource Groups is a simple yet powerful way to automate your cloud infrastructure. By following best practices and leveraging Terraform’s features, you can ensure your resources are organized, consistent, and easy to manage.
Start small and gradually expand your Terraform configurations to include more complex resources and dependencies.
# Example: Destroying the resource group
terraform destroy
With Terraform, managing your Azure infrastructure becomes efficient and scalable, allowing you to focus on building great applications.