When deploying applications in the cloud, understanding the concept of regions and availability zones is crucial for ensuring high availability, performance, and resilience. Azure, Microsoft’s cloud platform, organizes its global infrastructure into regions, which are physical locations around the world where data centers are clustered. Each region is designed to provide redundancy and low-latency access to users in its vicinity.
What are Azure Regions?
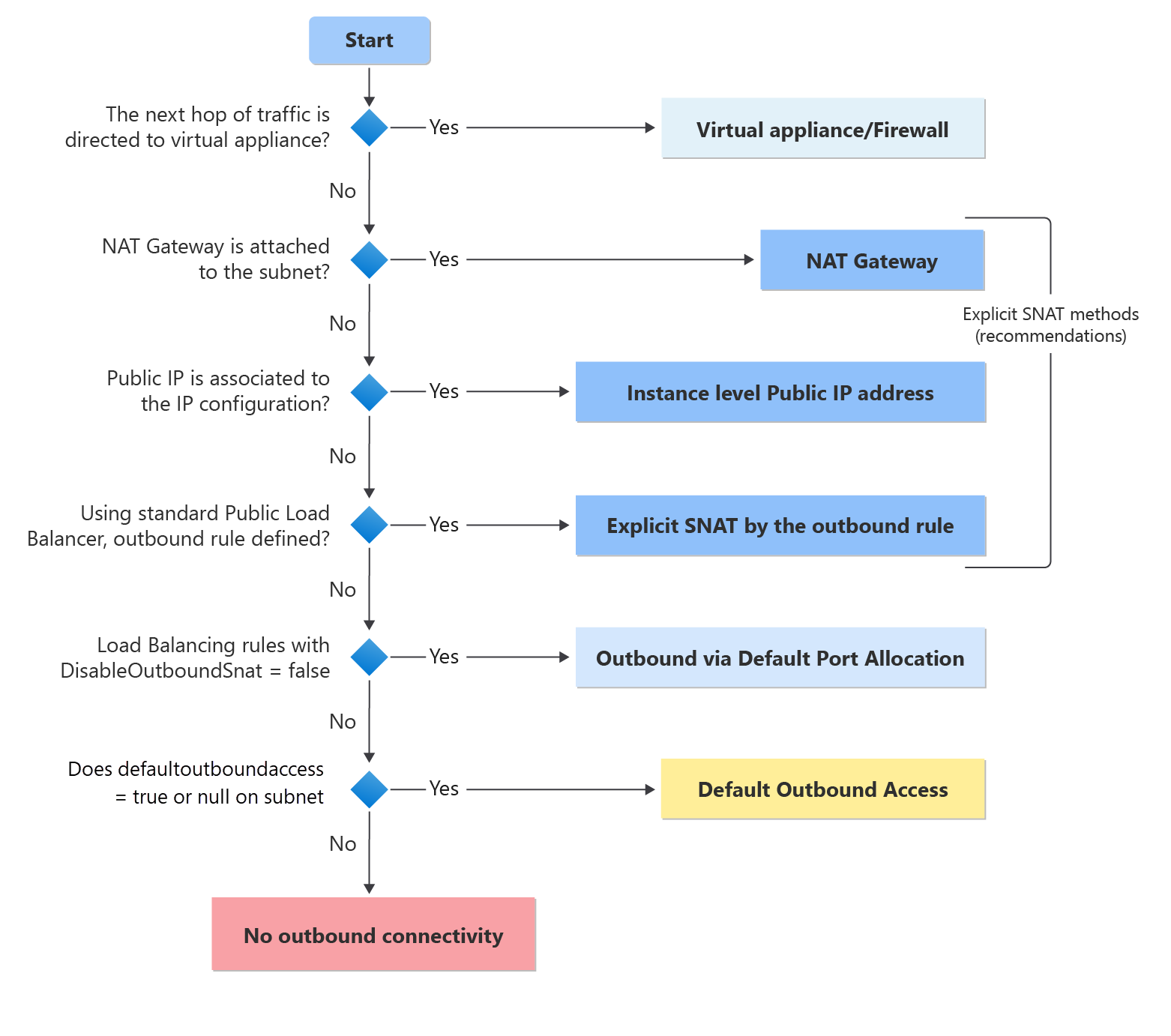
Azure regions are geographic areas that contain one or more data centers. These regions allow you to deploy resources close to your users, reducing latency and improving performance. For example, if your users are primarily in Europe, deploying your application in an Azure region like “West Europe” or “North Europe” ensures faster response times.
Learn more about Azure regions
Choosing the right Azure region can significantly impact your application’s performance and compliance with data residency requirements.
Availability Zones: Enhancing Resilience
Within each Azure region, availability zones provide an additional layer of fault tolerance. An availability zone is a physically separate location within a region, with its own independent power, cooling, and networking. By distributing your resources across multiple availability zones, you can protect your applications from data center failures and ensure business continuity.
Learn more about Azure availability zones
 Photo by Cayetano Gros on Lummi
Photo by Cayetano Gros on Lummi
Azure’s architecture ensures that even in the event of a failure in one availability zone, your application can continue running seamlessly in another. This makes availability zones a key feature for mission-critical workloads that require high availability and disaster recovery.
“The strength of the cloud lies in its ability to adapt and recover from failures, ensuring uninterrupted service for users.”
Understanding Azure regions and availability zones is essential for designing robust cloud solutions. By leveraging these features, you can optimize performance, meet compliance requirements, and build resilient applications that scale globally.